[Dev] Web Sockets
Client Server Connection - Limitation of HTTP
The issue with HTTP is that only the client can initiate the connection. For instance, if userA wants to send a message, they can use the HTTP protocol to connect to the backend and send the message. However, the backend cannot send a HTTP request to userB. This creates a problem when userA wants to send a message to userB. How can userB be notified that userA has sent a message? There are several options available to solve this problem, namely Polling, Long Polling, and WebSockets. Let’s explore each protocol and determine the best option for sending messages between different users.
Polling
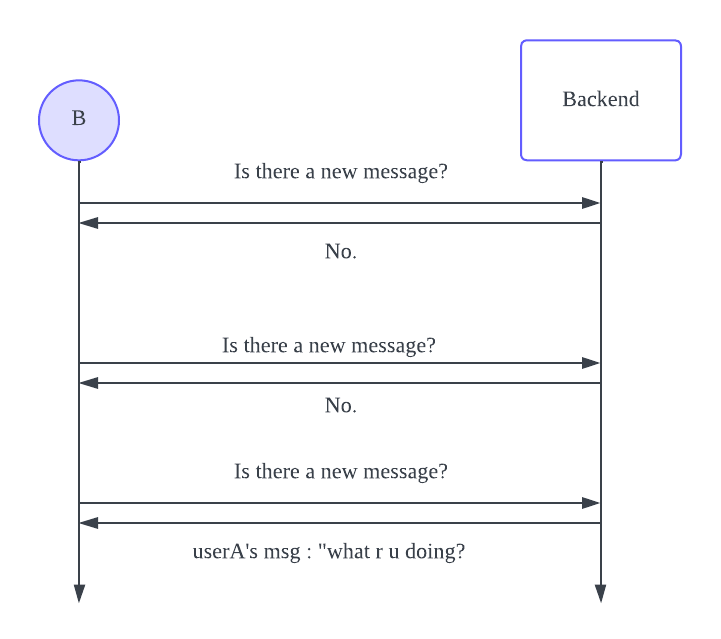
When using the HTTP protocol, the backend cannot directly send a HTTP request to userB. Polling is a method where userB repeatedly asks the backend if there are any new messages. The backend will inform userB whether there is a message to receive or not. This means that when userA sends a message to the backend, userB can receive the message by asking the backend.
However, there are some limitations to using polling. In most cases, the backend’s response when asked about new messages will be ‘no.’ Despite this, userB has to keep asking the backend for new messages, which increases the number of requests and raises the cost of the backend infrastructure. Additionally, there is a delay in message delivery. If userB asks the backend every second, there will be a 1-second delay before userB knows that userA has sent a message to the backend, resulting in message latency.
Long Polling
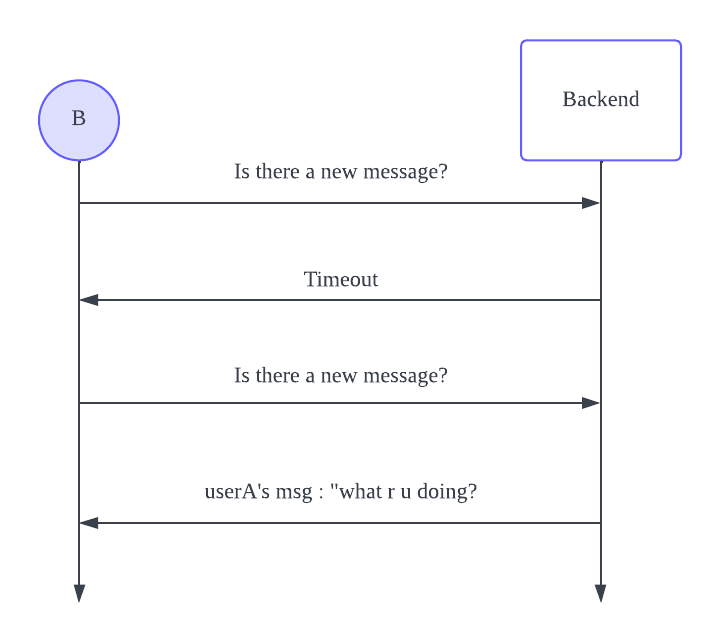
Long polling works differently from polling. When userB makes a request, the backend doesn’t immediately send a response. Instead, it waits until a timeout occurs. If a timeout occurs, the backend sends a timeout response to userB. At that point, userB can make another request to the backend. If a message has been received by the backend before the timeout, it sends the received message back to userB. Long polling is similar to polling but reduces the number of requests. However, there are still a significant number of requests sent to the backend, and message latency remains a concern.
Server-Sent Events (SSE)
Server-Sent Events operates based on the HTTP protocol and works in a unidirectional manner, where data is sent from the server to the client. It can be useful for tasks that involve pushing server events or messages to clients. Therefore, it would be beneficial to use for updating real-time data such as trending keywords, weather information, or email updates.
WebSockets
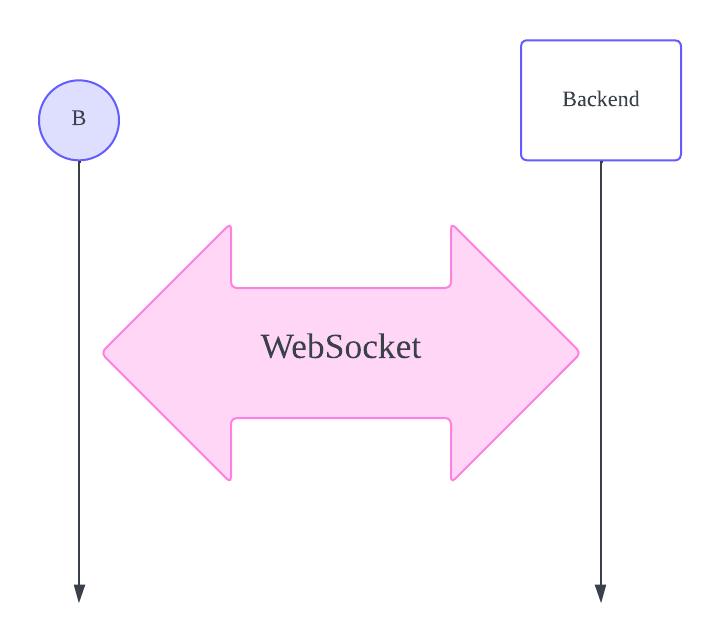
To enable real-time communication services, WebSockets provide a solution. WebSockets function differently from the HTTP protocol. Unlike HTTP, which terminates the connection after receiving a response, WebSockets maintain an open connection. WebSocket is a protocol based on the HTML5 standard technology that allows bidirectional real-time communication between a client and a server over a single TCP connection in the HTTP environment.
1. Web Socket Handshake
WebSocket starts communication with an HTTP handshake, and then converts to the WebSocket protocol to transmit data. Initially, the client sends a handshake request to the server using the HTTP protocol. This protocol uses the upgrade header to switch from the HTTP protocol to the WebSocket protocol.
2. Ws vs Wss
Ws is does not support secure connections, but wss supports secure connections.
3. Port for WebSocket
WebSocket does not need to open a separate port.
- Operates on top of HTTP port 80, HTTPS port 443.